

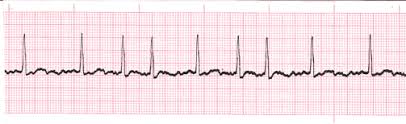
Atrial fibrillation (AF or A-fib) is a type of arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythm) characterised by rapid and irregular beating of the heart's atrial chambers. It frequently begins with brief periods of abnormal breathing that gradually become longer or continuous. It may also begin as another type of arrhythmia, such as atrial flutter, and then progress to AF. Asymptomatic episodes are possible. Symptoms include palpitations, fainting, light-headedness, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of heart failure and dementia, stroke. It is classified as supraventricular tachycardia.
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Allied Academies Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by
